Player FM 앱으로 오프라인으로 전환하세요!
Episode 181.0: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
저장한 시리즈 ("피드 비활성화" status)
When?
This feed was archived on January 25, 2023 12:04 (
Why? 피드 비활성화 status. 잠시 서버에 문제가 발생해 팟캐스트를 불러오지 못합니다.
What now? You might be able to find a more up-to-date version using the search function. This series will no longer be checked for updates. If you believe this to be in error, please check if the publisher's feed link below is valid and contact support to request the feed be restored or if you have any other concerns about this.
Manage episode 286541659 series 1415404
We discuss EM presentation, diagnosis, and management of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Hosts:
Mark Iscoe, MD
Brian Gilberti, MD
Bree Tse, MD
Show Notes
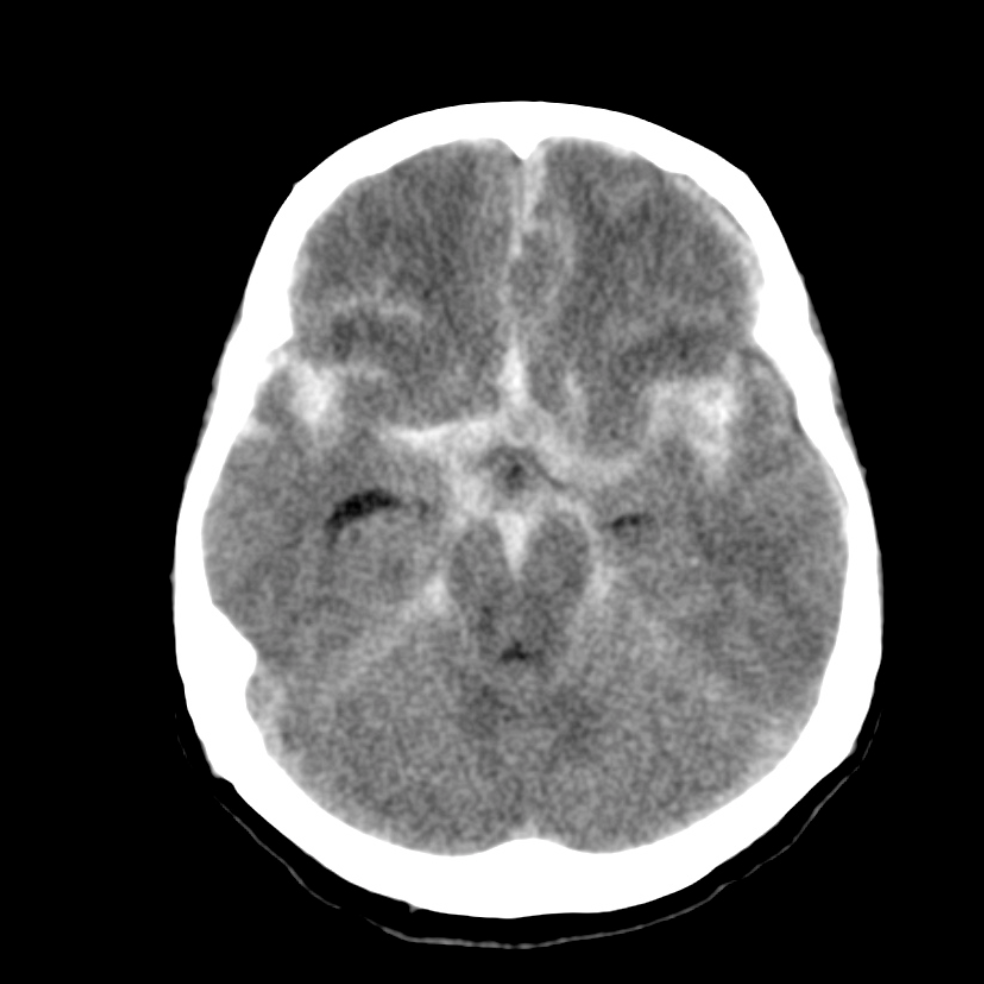
Non-contrast head CT showing SAH (Case courtesy of Dr. David Cuete, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 22770)
Hunt-Hess grade and mortality (from Lantigua et al. 2015.)
| Hunt-Hess grade | Mortality (%) |
| 1. Mild Headache | 3.5 |
| 2. Severe headache or cranial nerve deficit | 3.2 |
| 3. Confusion, lethargy, or lateralized weakness | 9.4 |
| 4. Stupor | 23.6 |
| 5. Coma | 70.5 |
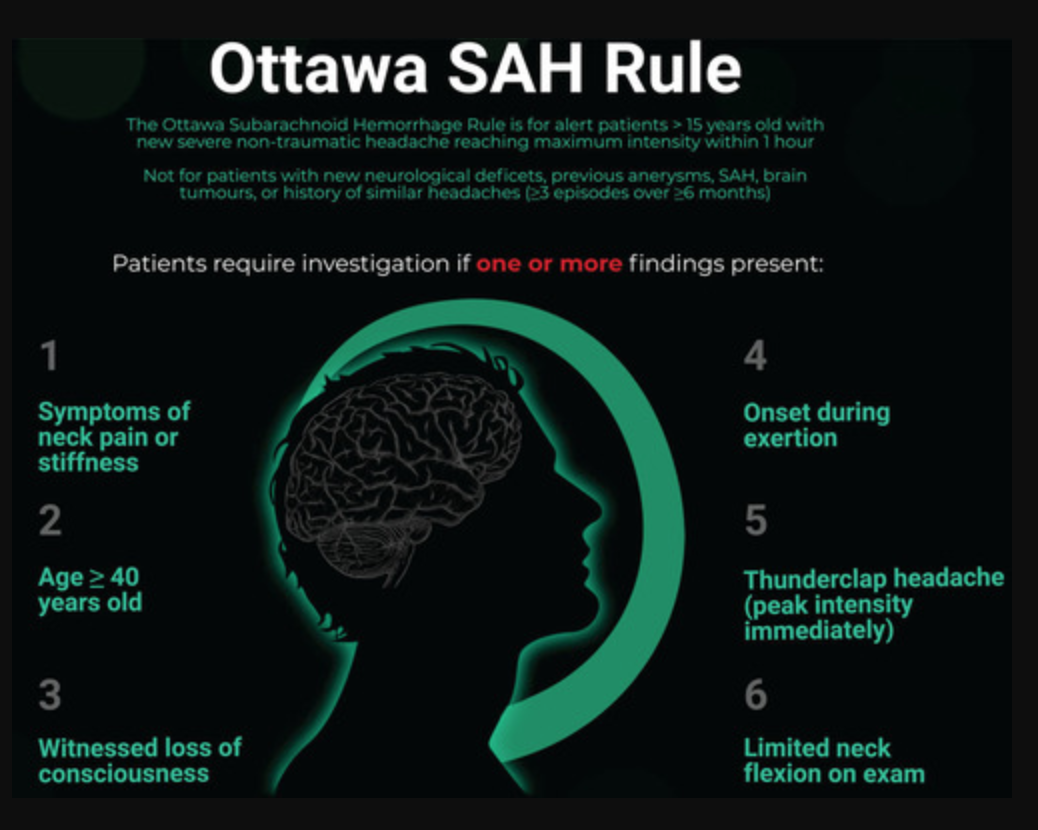
Ottawa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Rule, and appropriate population for rule application (from Perry et al. 2017)
Apply to patients who are:
- Alert
- ≥ 15 years old
- Have new, severe, atraumatic headache that reached maximum intensity within 1 hour of osnet
Do not apply to patients who have:
- New neurologic deficits
- Previous diagnosis of intracranial aneurysm, SAH, or brain tumor
- History of similar headaches (≥ 3 episodes over ≥ 6 months)
SAH cannot be ruled out if the patient meets any of the following criteria:
- Age ≥ 40
- Symptom of neck pain or stiffness
- Witnessed loss of consciousness
- Onset during exertion
- “Thunderclap headache” (defined as instantly peaking pain)
- Limited neck flexion on examination (defined as inability to touch chin to chest or raise head 3 cm off the bed if supine)
___________________________
Special Thanks To:
- Dr. Mark Iscoe, MD (Ronald O. Perelman Department of Emergency Medicine at NYU Langone Health, NYC Health + Hospitals/ Bellevue)
___________________________
References:
Bellolio MF, Hess EP, Gilani WI, et al. External validation of the Ottawa subarachnoid hemorrhage clinical decision rule in patients with acute headache. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(2):244-9.
Carstairs SD, Tanen DA, Duncan TD, et al. Computed tomographic angiography for the evaluation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acad Emerg Med. 2006;13(5):486-492.
Connolly ES, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012;43(6):1711-1737.
Czuczman AD, Thomas LE, Boulanger AB, et al. Interpreting red blood cells in lumbar puncture: distinguishing true subarachnoid hemorrhage from traumatic tap. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20(3):247-256.
Dugas C, Jamal Z, Bollu PC. Xanthochromia. [Updated 2020 Aug 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526048/
Goldstein JN, Camargo CA, Pelletier AJ, Edlow JA. Headache in United States emergency departments: demographics, work-up and frequency of pathological diagnoses. Cephalalgia. 2006;26(6):684-90.
Kumar A, Niknam K, Lumba-brown A, et al. Practice Variation in the Diagnosis of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Survey of US and Canadian Emergency Medicine Physicians. Neurocrit Care. 2019.
Lantigua H, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Schmidt JM, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: who dies, and why? Crit Care. 2015;19:309.
Macdonald RL, Schweizer TA. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):655-666.
Mayer PL, Awad IA, Todor R, et al. Misdiagnosis of symptomatic cerebral aneurysm. Prevalence and correlation with outcome at four institutions. Stroke. 1996;27(9):1558-63.
Meurer WJ, Walsh B, Vilke GM, Coyne CJ. Clinical guidelines for the emergency department evaluation of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Emerg Med. 2016;50(4):696-701.
Perry JJ, Spacek A, Forbes M, et al. Is the combination of negative computed tomography result and negative lumbar puncture result sufficient to rule out subarachnoid hemorrhage? Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51(6):707-713
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti MLA, et al. High risk clinical characteristics for subarachnoid haemorrhage in patients with acute headache: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2010;341:c5204.
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti MLA, et al. Sensitivity of computed tomography performed within six hours of onset of headache for diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2011;343(jul18 1):d4277-d4277.
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti ML, et al. Clinical decision rules to rule out subarachnoid hemorrhage for acute headache. JAMA. 2013;310(12):1248-55.
Perry JJ, Sivilotti MLA, Sutherland J, et al. Validation of the Ottawa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Rule in patients with acute headache. CMAJ. 2017;189(45):E1379-E1385.
Vermeulen MJ, Schull MJ. Missed diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the emergency department. Stroke. 2007;38(4):1216-21.
Read More
243 에피소드
저장한 시리즈 ("피드 비활성화" status)
When?
This feed was archived on January 25, 2023 12:04 (
Why? 피드 비활성화 status. 잠시 서버에 문제가 발생해 팟캐스트를 불러오지 못합니다.
What now? You might be able to find a more up-to-date version using the search function. This series will no longer be checked for updates. If you believe this to be in error, please check if the publisher's feed link below is valid and contact support to request the feed be restored or if you have any other concerns about this.
Manage episode 286541659 series 1415404
We discuss EM presentation, diagnosis, and management of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Hosts:
Mark Iscoe, MD
Brian Gilberti, MD
Bree Tse, MD
Show Notes
Non-contrast head CT showing SAH (Case courtesy of Dr. David Cuete, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 22770)

Hunt-Hess grade and mortality (from Lantigua et al. 2015.)
| Hunt-Hess grade | Mortality (%) |
| 1. Mild Headache | 3.5 |
| 2. Severe headache or cranial nerve deficit | 3.2 |
| 3. Confusion, lethargy, or lateralized weakness | 9.4 |
| 4. Stupor | 23.6 |
| 5. Coma | 70.5 |
Ottawa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Rule, and appropriate population for rule application (from Perry et al. 2017)
Apply to patients who are:
- Alert
- ≥ 15 years old
- Have new, severe, atraumatic headache that reached maximum intensity within 1 hour of osnet
Do not apply to patients who have:
- New neurologic deficits
- Previous diagnosis of intracranial aneurysm, SAH, or brain tumor
- History of similar headaches (≥ 3 episodes over ≥ 6 months)
SAH cannot be ruled out if the patient meets any of the following criteria:
- Age ≥ 40
- Symptom of neck pain or stiffness
- Witnessed loss of consciousness
- Onset during exertion
- “Thunderclap headache” (defined as instantly peaking pain)
- Limited neck flexion on examination (defined as inability to touch chin to chest or raise head 3 cm off the bed if supine)

___________________________
Special Thanks To:
- Dr. Mark Iscoe, MD (Ronald O. Perelman Department of Emergency Medicine at NYU Langone Health, NYC Health + Hospitals/ Bellevue)
___________________________
References:
Bellolio MF, Hess EP, Gilani WI, et al. External validation of the Ottawa subarachnoid hemorrhage clinical decision rule in patients with acute headache. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(2):244-9.
Carstairs SD, Tanen DA, Duncan TD, et al. Computed tomographic angiography for the evaluation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acad Emerg Med. 2006;13(5):486-492.
Connolly ES, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012;43(6):1711-1737.
Czuczman AD, Thomas LE, Boulanger AB, et al. Interpreting red blood cells in lumbar puncture: distinguishing true subarachnoid hemorrhage from traumatic tap. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20(3):247-256.
Dugas C, Jamal Z, Bollu PC. Xanthochromia. [Updated 2020 Aug 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526048/
Goldstein JN, Camargo CA, Pelletier AJ, Edlow JA. Headache in United States emergency departments: demographics, work-up and frequency of pathological diagnoses. Cephalalgia. 2006;26(6):684-90.
Kumar A, Niknam K, Lumba-brown A, et al. Practice Variation in the Diagnosis of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Survey of US and Canadian Emergency Medicine Physicians. Neurocrit Care. 2019.
Lantigua H, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Schmidt JM, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: who dies, and why? Crit Care. 2015;19:309.
Macdonald RL, Schweizer TA. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):655-666.
Mayer PL, Awad IA, Todor R, et al. Misdiagnosis of symptomatic cerebral aneurysm. Prevalence and correlation with outcome at four institutions. Stroke. 1996;27(9):1558-63.
Meurer WJ, Walsh B, Vilke GM, Coyne CJ. Clinical guidelines for the emergency department evaluation of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Emerg Med. 2016;50(4):696-701.
Perry JJ, Spacek A, Forbes M, et al. Is the combination of negative computed tomography result and negative lumbar puncture result sufficient to rule out subarachnoid hemorrhage? Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51(6):707-713
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti MLA, et al. High risk clinical characteristics for subarachnoid haemorrhage in patients with acute headache: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2010;341:c5204.
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti MLA, et al. Sensitivity of computed tomography performed within six hours of onset of headache for diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2011;343(jul18 1):d4277-d4277.
Perry JJ, Stiell IG, Sivilotti ML, et al. Clinical decision rules to rule out subarachnoid hemorrhage for acute headache. JAMA. 2013;310(12):1248-55.
Perry JJ, Sivilotti MLA, Sutherland J, et al. Validation of the Ottawa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Rule in patients with acute headache. CMAJ. 2017;189(45):E1379-E1385.
Vermeulen MJ, Schull MJ. Missed diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the emergency department. Stroke. 2007;38(4):1216-21.
Read More
243 에피소드
모든 에피소드
×플레이어 FM에 오신것을 환영합니다!
플레이어 FM은 웹에서 고품질 팟캐스트를 검색하여 지금 바로 즐길 수 있도록 합니다. 최고의 팟캐스트 앱이며 Android, iPhone 및 웹에서도 작동합니다. 장치 간 구독 동기화를 위해 가입하세요.




